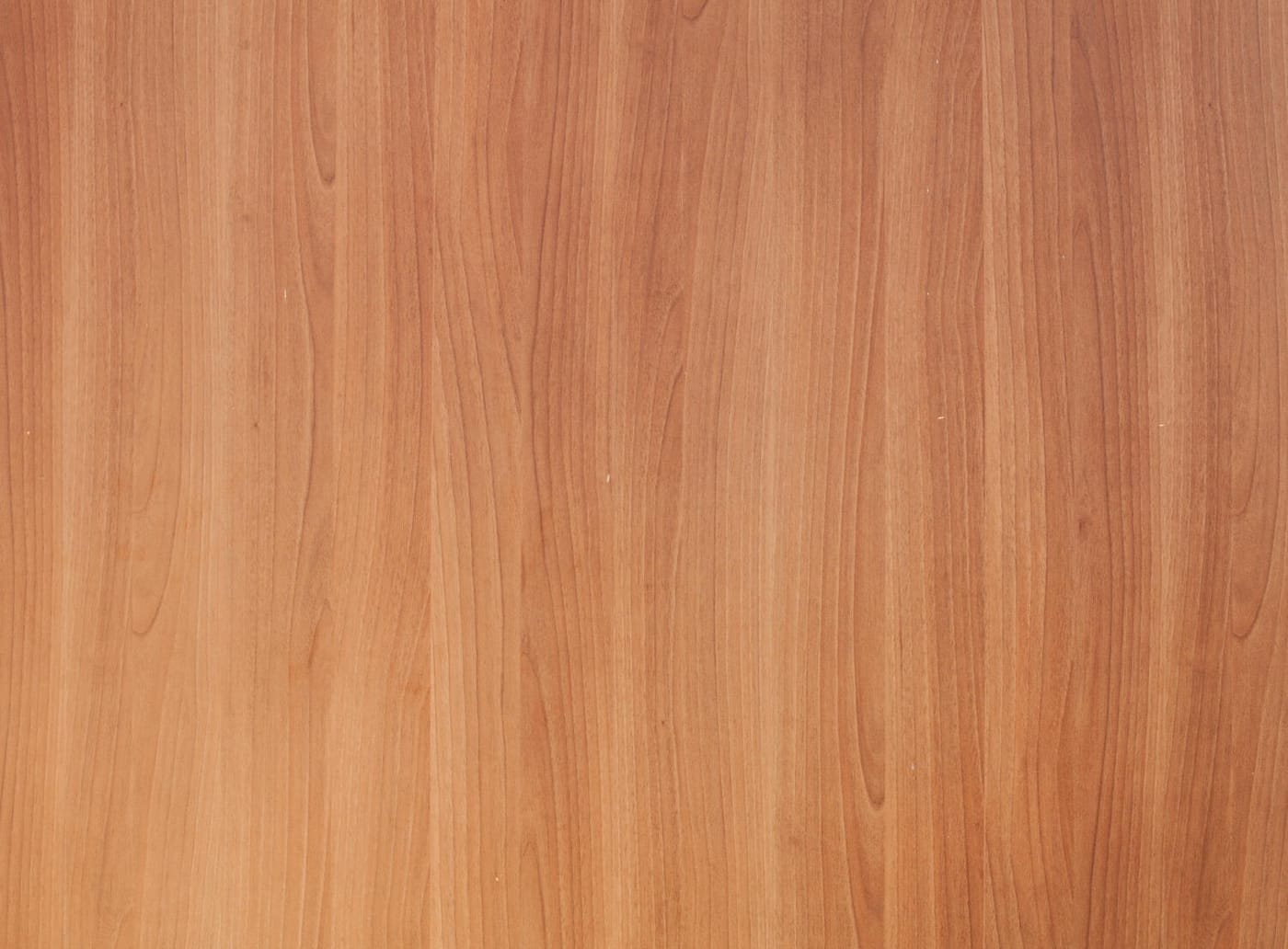


Laminated wood is an engineered material made by bonding multiple layers of wood together to create a stronger, more stable, and durable surface than solid wood.
Laminated wood is a widely used material in modern furniture, interior design, and construction, valued for its strength, stability, and versatility.
Created by bonding multiple layers of wood together, it provides a durable and cost-effective alternative to solid wood while maintaining a clean, uniform appearance. Understanding what laminated wood is helps explain why it has become a preferred choice for both residential and commercial applications.
What is Laminated Wood?
Laminated wood is an engineered wood product made by bonding multiple layers of wood or wood-based materials using high-strength adhesives. These layers form a single, stable panel that offers improved durability and performance.
Its layered construction minimizes common issues associated with solid wood, such as warping, shrinking, and cracking, especially in environments with changing temperatures or humidity.
Laminated wood is important because it delivers consistent quality, efficient use of natural resources, and flexible design options, which make it a reliable material for furniture, interiors, and modern construction projects.
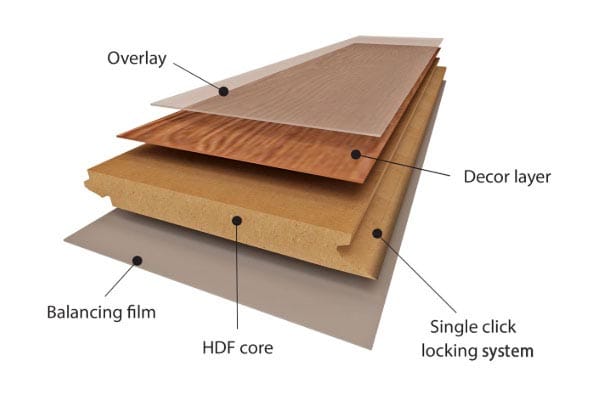
How Laminated Wood is Made
The production of laminated wood begins with carefully selected thin wood sheets (veneers) or wood fibers. Each layer is prepared and coated with a strong adhesive, typically a durable resin or wood glue designed for long-term bonding.
The layers are then stacked together, often with their grain directions alternated to enhance strength and reduce the risk of warping. Once assembled, the stacked layers are pressed under high pressure and, in some cases, heat to form a solid, unified panel.
After pressing, the laminated wood is trimmed, sanded, and finished to achieve a smooth, consistent surface. Some panels are further enhanced with a decorative veneer or laminate layer, improving appearance while adding resistance to scratches, moisture, and stains.
This manufacturing process allows producers to create large, uniform, and durable panels suitable for furniture, cabinetry, flooring, doors, and even structural applications—all while using wood resources efficiently and minimizing material waste.
Advantages of Laminated Wood
Laminated wood offers several benefits that make it a popular choice for furniture, interiors, and construction:
Strength and stability
One of the key advantages of laminated wood is its enhanced strength and long-term stability. The layered construction, combined with alternating grain directions and high-strength adhesives, distributes stress evenly across the material. This significantly reduces the risk of warping, cracking, or shrinking compared to solid wood.
As a result, laminated wood is well-suited for high-use and load-bearing applications such as furniture, flooring, and structural components.It ensures the material maintains its shape, reliability, and performance over time.
Resistance to warping, cracking, and shrinking
Laminated wood is designed to withstand changes in temperature and humidity better than solid wood. Its multi-layered construction, reinforced with strong adhesives, helps balance internal stress and maintain structural integrity.
This design greatly reduces the risk of warping, cracking, or shrinking that commonly affects solid wood over time. This makes laminated wood a reliable choice for furniture, cabinetry, flooring, and other applications where durability and long-term performance are essential.
Eco-friendly option
Laminated wood is regarded as an eco-friendly material because it maximizes the efficient use of natural resources. Manufacturers turn thin veneers and smaller wood materials into durable panels, which reduces the need for large solid logs.
This efficient use of wood reduces waste, lowers overall timber consumption, and helps minimize environmental impact. As a result, laminated wood is a more sustainable alternative for furniture, cabinetry, and construction projects. It supports modern design needs while promoting responsible material use.
Versatility in shapes and sizes
Laminated wood offers remarkable versatility in design, which allows manufacturers to create panels, beams, and boards in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Its engineered structure makes it suitable for curved surfaces, large spans, and custom dimensions that would be difficult or costly to achieve with solid wood.
For example, many Apple retail stores use laminated wood panels and beams in their interiors to create sleek, modern ceilings and furniture that are both durable and visually appealing.
This flexibility makes laminated wood ideal for furniture, cabinetry, flooring, and even architectural or structural applications.
Disadvantages of Laminated Wood
While laminated wood offers many benefits, it also comes with certain limitations that are important to consider before choosing it for furniture, interiors, or construction projects.
Expensive
High-quality laminated wood can sometimes be more expensive than standard solid wood or other engineered wood products. This is especially true for laminated panels that use premium veneers, specialized adhesives, or advanced manufacturing processes. While the investment often pays off in durability and stability, the initial cost may be a consideration for budget-conscious projects.
Susceptible to moisture damage
Laminated wood can be vulnerable to moisture if it is not properly sealed or finished. Prolonged exposure to water or high humidity can weaken the adhesive layers, causing swelling, delamination, or warping. This makes it important to use laminated wood in controlled environments or ensure it has protective coatings for areas prone to moisture, such as kitchens, bathrooms, or outdoor applications.
Limited natural appearance
Unlike solid wood, laminated wood may have a less authentic or uniform natural look, since it is made by layering veneers or engineered wood sheets. While decorative laminates can mimic the appearance of real wood, stone, or other textures, they may lack the unique grain patterns and character that many people appreciate in natural wood.
For projects where the visual appeal of natural wood is a priority, this limitation may influence material choice. However, laminated wood remains a practical option for modern interiors where consistency, durability, and cost-effectiveness are important.
Chemical concerns
While laminated wood is durable and versatile, some products are manufactured using adhesives, glues, or resins that may contain formaldehyde or other volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Over time, these chemicals can off-gas, potentially impacting indoor air quality and causing health concerns, particularly in poorly ventilated spaces.
The level of chemical emissions can vary depending on the type of adhesive, the quality of the laminates, and the manufacturing standards. To ensure safety, it is important to choose laminated wood products that are low-VOC, CARB-compliant, or certified formaldehyde-free.
Proper ventilation and finishing treatments can further reduce exposure. This makes laminated wood a safer option for homes, schools, and offices without compromising its strength, stability, or appearance.
Common Uses of Laminated Wood
Laminated wood is a versatile material used in a wide range of applications across furniture, interiors, and construction. Its long-lasting performance, structural integrity, and customizable design make it suitable for both residential and commercial projects.
Some of the most common uses include:
Furniture
Laminated wood is widely used in furniture making because it combines durability with design flexibility. Its strength, stability, and customizable finishes make it ideal for both residential and commercial spaces.
A notable example is the laminated bent wood furniture designed for WeWork’s NYC WeGrow education space, where tables and chairs were crafted from laminated Baltic birch plywood to meet modern design and functional requirements.
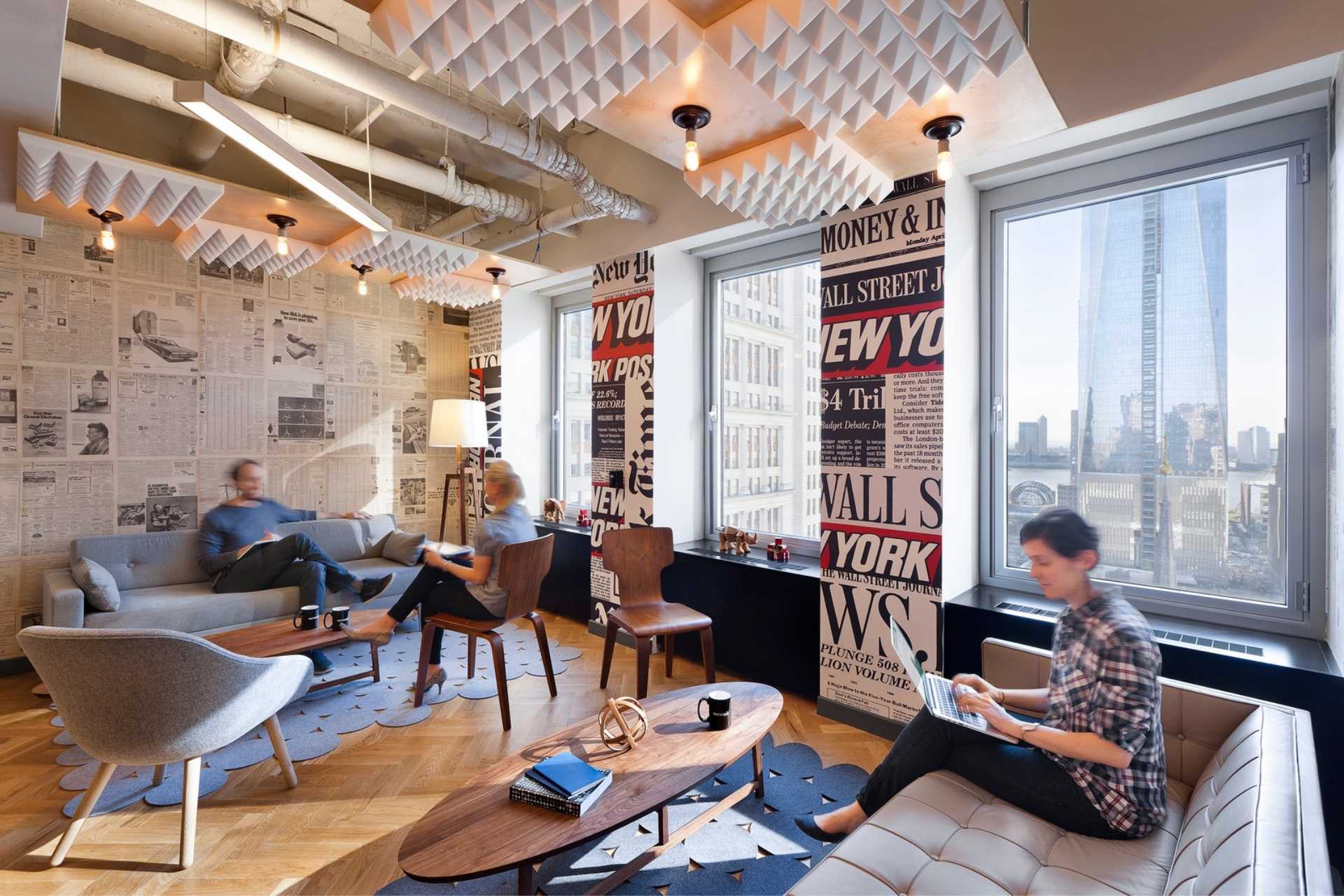

Laminated wood is popular in New York for modern apartments, office interiors, and boutique furniture stores, where designers value its durability, cost-effectiveness, and sleek appearance.
Beams, flooring, bridges
Laminated wood is also used in structural and construction applications due to its strength and stability. Products like glued laminated timber (glulam) and laminated veneer lumber (LVL) are ideal for beams, flooring, and even pedestrian bridges.
Their engineered layers allow them to span long distances without bending or warping. This makes laminated wood a reliable choice for modern buildings and infrastructure projects.
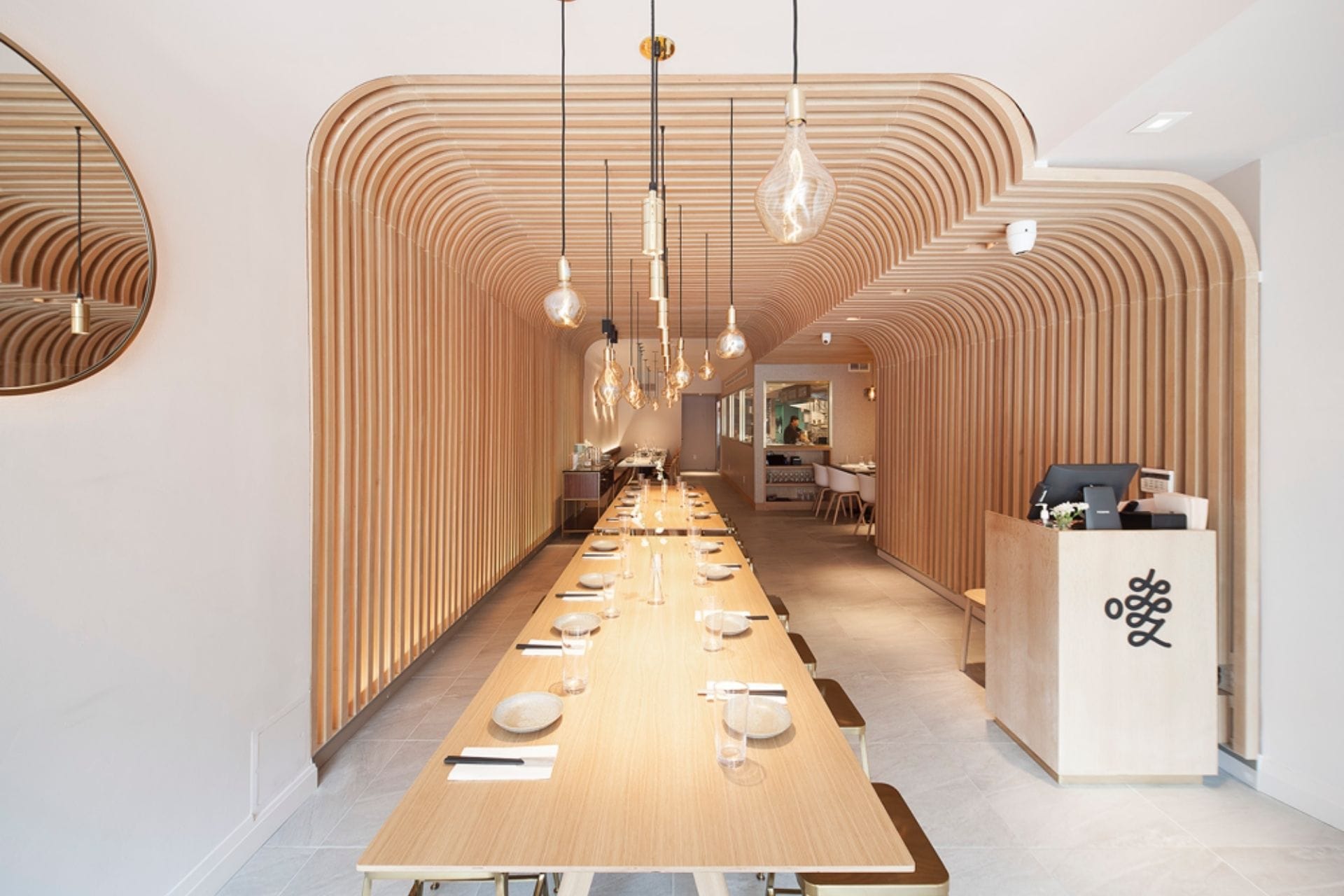
Interior design
Laminated wood is a popular choice in interior design.
In New York City, designers often use wood slats and laminated wood finishes to create inviting, contemporary interiors. A great example is Hunan Slurp in the East Village. The restaurant’s interior is wrapped in wood slats that line walls and ceilings, which adds warmth and dynamic texture to the dining space.

Laminated Wood Care and Maintenance Tips
Proper care and maintenance can extend the life and appearance of laminated wood for years. Here are some practical tips:
- Regular Cleaning: Wipe laminated surfaces with a soft, damp cloth. Avoid abrasive cleaners or scrubbers that can scratch the finish.
- Avoid Excess Moisture: Protect laminated wood from prolonged water exposure. Quickly wipe up spills to prevent swelling or delamination.
- Use Protective Pads: Place felt pads under furniture legs to prevent scratches and dents on laminated flooring or surfaces.
- Limit Direct Sunlight: Prolonged exposure to sunlight can fade the color of laminated surfaces. Use curtains or blinds to reduce UV damage.
- Avoid Harsh Chemicals: Stick to mild cleaning solutions or products specifically designed for laminated wood.
- Temperature Control: Keep laminated wood away from extreme heat sources, such as radiators or direct heat vents, to prevent warping or damage to adhesives.
Summary
Laminated wood combines strength, style, and versatility. This makes it an ideal option for modern furniture, architectural interiors, and structural applications. Its durability, consistent appearance, and eco-friendly advantages make it a practical and reliable alternative to solid wood. With proper care, laminated wood can maintain its beauty and performance for years, which offers a long-lasting solution that meets both functional and aesthetic needs.
Transform your space with the strength and style of laminated wood. Work with New York’s trusted commercial furniture installation experts and explore Artistic Display’s custom modern collection to create interiors that combine functionality and timeless style.